Following our longitudinal study of Utility and Rental Metadata, this research explores Student Loan Auditing as a direct systemic consequence. The previous analysis established how consistent payment rhythms in non-debt obligations calibrate baseline reliability; however, the long-term structural pressure of educational credit introduces complex psychological variables. Therefore, this study examines how 2026 oversight mechanisms interpret shifting repayment behaviors as discrete markers of cognitive state transitions.
The Mechanics of Student Loan Auditing in 2026
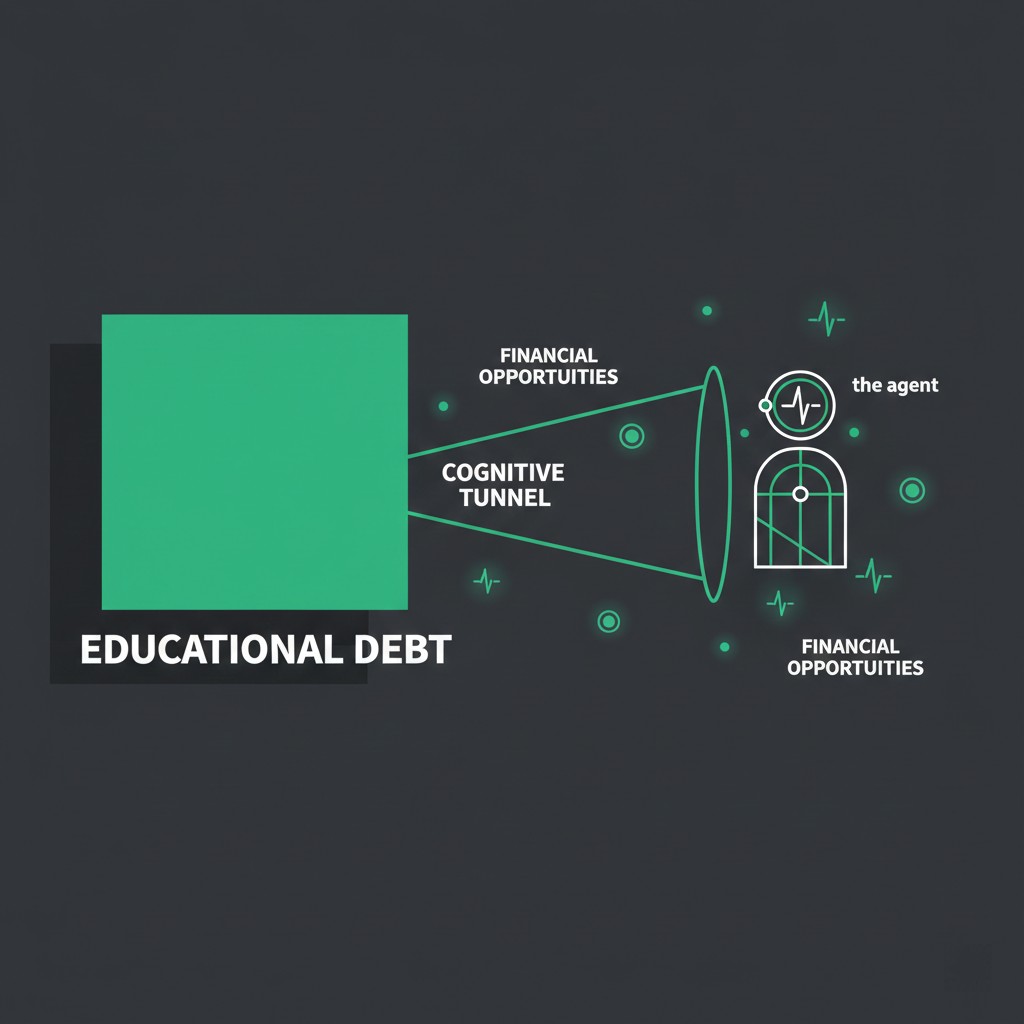
In the 2026 macro-prudential landscape, Student Loan Auditing focuses on identifying “Cognitive Tunneling” within borrower profiles. This behavioral finance phenomenon occurs when long-term debt pressure narrows an agent’s financial focus, leading to suboptimal decision-making in other credit domains. Systemic mechanics evaluate the interaction between student debt service ratios and the sudden neglect of small-scale administrative obligations.
Institutional models utilize metadata flow observation to detect these behavioral inflection points. For instance, a profile that maintains consistent student loan payments but demonstrates increasing entropy in minor utility settlements triggers a specialized review. Consequently, the probabilistic evaluation layer classifies this divergence as a latent risk marker, suggesting that the agent is prioritizing high-consequence debt at the cost of overall balance-sheet health.
Cognitive Tunneling and Probabilistic Evaluation
The integration of behavioral markers into Student Loan Auditing allows systems to predict state transitions before a formal default occurs. Behavioral recurrence patterns reveal that agents under severe educational debt pressure often exhibit a “Relief Trap” signature—using short-term revolving credit to sustain long-term loan obligations. Therefore, the system interprets these patterns as an erosion of structural consistency.
The Federal Reserve has analyzed how student debt structures influence systemic mobility. Data correlates more strongly with the persistence of the debt-to-income ratio than with the absolute balance. Consequently, the systemic review process monitors the “velocity of repayment” relative to career progression metadata. If the repayment trajectory stagnates despite income growth, the system identifies a financial inflection point that may limit future mortgage or auto-credit availability.
Systemic Mechanics of Debt Prioritization
Probability-based auditing identifies how agents prioritize their obligations during periods of transient market noise. Within the framework of Student Loan Auditing, the system monitors for “Strategic Friction”—intentional delays in payment designed to preserve immediate liquidity. Moreover, the oversight mechanism cross-references these delays with the agent’s digital footprint to ensure the narrative remains consistent with the modeled balance-sheet condition.
In contrast to legacy scoring, 2026 models prioritize the stability of the repayment environment. As a result, agents who utilize income-driven repayment metadata as a strategic tool rather than a crisis response maintain a more robust statistical relationship with lending algorithms. This is a general educational framework, not personalized financial advice. We are not a credit bureau, lender, or scoring model provider.
Navigating the Educational Credit Nexus
To analyze how systemic review engines weight long-term educational obligations, researchers utilize our resources page as an analytical modeling aid. Managing the metadata associated with student debt requires an understanding of how behavioral credit auditing shift 2026 logic evaluates the coherence of financial signals.
The system favors profiles that demonstrate a predictable, non-volatile approach to debt amortization. Moreover, the strategic alignment of educational investment with career-based metadata flows enhances the profile’s structural integrity. Therefore, maintaining a stable trajectory in Student Loan Auditing involves projecting a cognitive state of long-term planning rather than short-term survivalism.
Conclusion: Behavioral States in Amortization
The reliance on systemic mechanics to monitor student debt confirms a shift in credit reversion behavior. Systems no longer view educational loans as static liabilities; instead, they function as dynamic sensors of an agent’s cognitive and financial resilience. Consequently, the resilience of a credit profile in 2026 depends on its ability to avoid the relief trap and maintain a consistent, modeled state of solvency throughout the amortization lifecycle.
Research Abstract
This research examines the behavioral finance implications of Student Loan Auditing in 2026. It identifies “Cognitive Tunneling” as a key systemic risk marker and analyzes how AI-driven oversight mechanisms detect shifts in repayment behavior as indicators of broader liquidity friction and modeled state transitions.
| Modeled State | Behavioral Marker | Systemic Response |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Consistency | Predictable amortization/income alignment | Probability-based baseline maintained |
| Cognitive Tunneling | Hyper-focus on loan vs. minor defaults | Latent risk marker applied |
| Relief Trap State | Revolving credit use for loan service | Discrete state recognition: Volatility |
Data Accuracy Note (2026): Market conditions, Federal Reserve interest rates, and lender algorithms change rapidly. While we strive to provide the most accurate insights as of January 2026, we recommend verifying all specific loan terms and APRs directly with your chosen platform before signing any agreement.